Is Neuroscience A Biological Science? Examining The Interdisciplinary Field
Neuroscience, the study of the nervous system, is a rapidly advancing interdisciplinary field that integrates biology, chemistry, psychology and more. But is neuroscience itself a biological science? In this 3000-word article, we’ll analyze neuroscience’s biological roots and modern interdisciplinary nature.
If you’re short on time, here’s the quick answer: Yes, neuroscience is generally considered a subfield within the biological sciences, as it involves applying the scientific method to study the biology of the nervous system.
Defining Biological Sciences
Biological sciences encompass the study of living organisms and their interactions within the natural world. It is a branch of science that seeks to understand the complexity and diversity of life, from the molecular level to entire ecosystems.
By exploring the fundamental processes and structures that underlie life, biological sciences provide valuable insights into the workings of the natural world.
Studying living organisms
Biologists employ a wide range of methods to study living organisms. They observe, experiment, and analyze data to uncover the intricate mechanisms that govern life processes. Through the use of microscopes, genetic sequencing techniques, and other advanced technologies, biologists are able to delve deeper into the mysteries of the natural world.
Methods of biology
Biologists use a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods to investigate living organisms. They collect data through observation and experimentation, and then analyze it using statistical tools and models.
This allows them to draw conclusions and make predictions about biological phenomena.
Categories of biological sciences
The field of biological sciences can be broadly categorized into several sub-disciplines. These include molecular biology, cellular biology, genetics, ecology, physiology, and evolutionary biology, among others.
Each sub-discipline focuses on a specific aspect of life, providing a comprehensive understanding of the biological world.
Interdisciplinary nature
Biological sciences are highly interdisciplinary, drawing upon knowledge and techniques from various fields such as chemistry, physics, mathematics, and computer science. This interdisciplinary approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of biological phenomena and fosters collaboration between different scientific disciplines.
For example, neurobiology, a sub-discipline of biology, combines elements of neuroscience, psychology, and physiology to study the nervous system and its impact on behavior and cognition. This interdisciplinary approach is crucial in unraveling the complexities of the human brain.
Neuroscience as a Biological Science
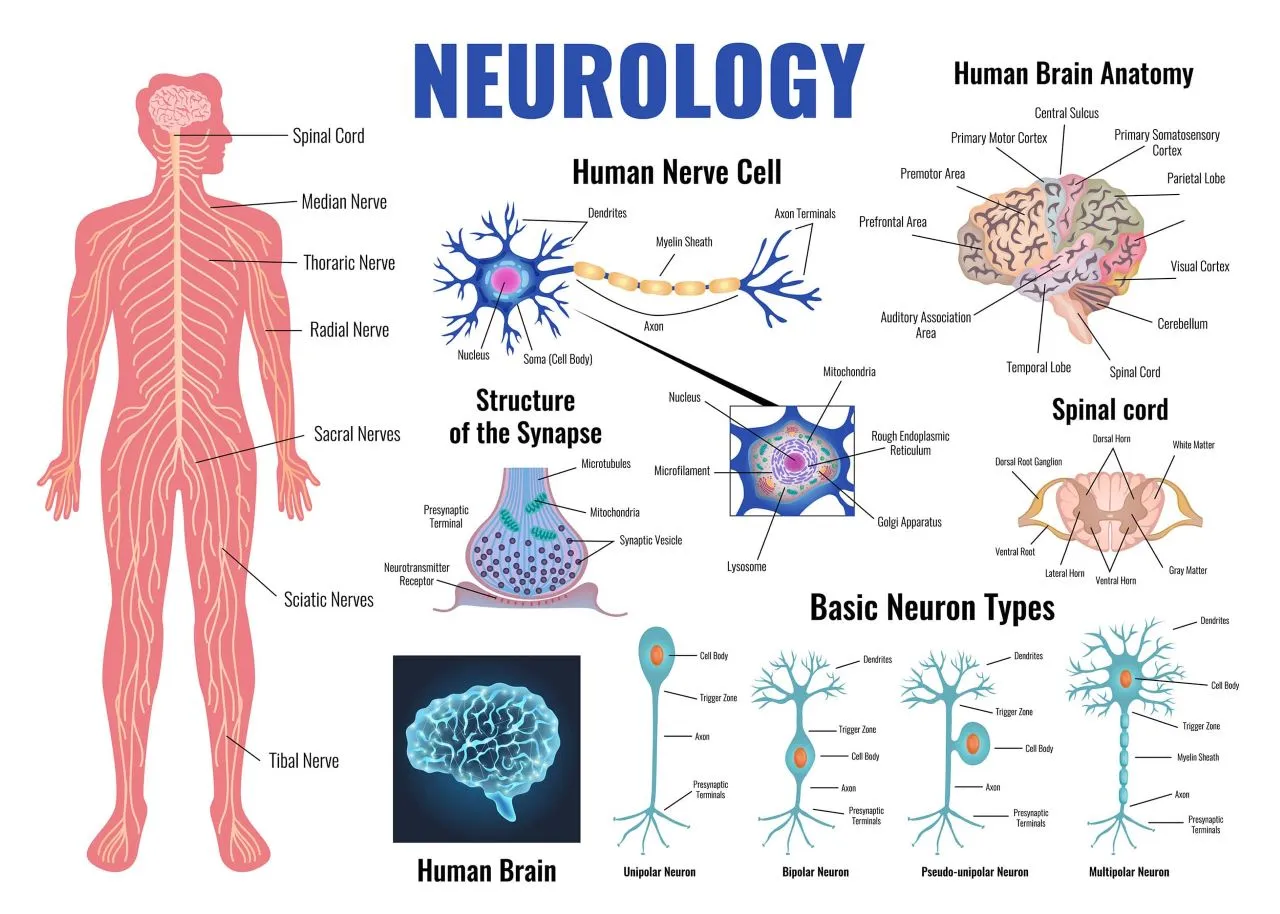
Neuroscience, as the name suggests, is the scientific study of the nervous system. It encompasses the study of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, and aims to understand how these complex systems function and interact with each other.
One could argue that neuroscience is indeed a biological science, as it primarily focuses on the biological aspects of the nervous system and its relationship with behavior and cognition.
Studies the nervous system
Neuroscientists investigate the structure and function of the nervous system at various levels, ranging from molecular and cellular to systems and behavioral neuroscience. They explore how neurons communicate with each other, how neural circuits are formed and maintained, and how these processes ultimately give rise to our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
By studying the nervous system, neuroscience contributes to our understanding of the biological basis of human experience.
Uses biological techniques
One of the defining features of neuroscience as a biological science is the wide range of techniques and methodologies it employs. Researchers in this field use a combination of approaches, including molecular biology, genetics, electrophysiology, imaging techniques, and behavioral experiments.
These techniques allow neuroscientists to investigate the intricate workings of the nervous system, providing valuable insights into its biological underpinnings.
Overlaps with other bio-fields
Neuroscience is an interdisciplinary field that draws upon knowledge and techniques from various biological sub-disciplines. It overlaps with fields such as physiology, anatomy, genetics, and pharmacology, to name just a few.
This collaboration between different branches of biology allows for a comprehensive understanding of the nervous system and its role in various biological processes.
Biological foundations predominate
While neuroscience encompasses a broad range of topics and approaches, its biological foundations predominate. The field is grounded in the principles of biology, focusing on the structure, function, and development of the nervous system.
By studying the biological aspects of the brain and behavior, neuroscientists contribute to our understanding of neurological disorders, mental health, and even the potential for enhancing cognitive abilities.
Aspects Beyond Biology
While neuroscience is primarily rooted in the biological sciences, there are several aspects of the field that extend beyond biology. These interdisciplinary connections allow for a more comprehensive understanding of the brain and its functions.
Here are some key areas where neuroscience intersects with other fields:
Integration of Psychological Science
Neuroscience and psychology have a strong relationship, with both fields focusing on the study of the mind and behavior. The integration of psychological science into neuroscience allows researchers to better understand how neural activity influences cognition, emotion, and behavior.
This collaboration between the two disciplines provides valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of mental processes and psychiatric disorders.
Uses of Chemistry
Chemistry plays a crucial role in neuroscience, particularly in the study of neurotransmitters and their receptors. Neurotransmitters are chemical substances that transmit signals across synapses, which are the gaps between nerve cells.
Understanding the chemistry of neurotransmitters helps neuroscientists unravel the intricate communication network within the brain. By studying the chemical processes involved, researchers can develop new drugs and treatments for neurological disorders.
Mathematical Modeling
Mathematical modeling is an essential tool in neuroscience, enabling scientists to simulate complex neural processes and understand brain function at various levels of detail. By employing mathematical equations and computational algorithms, researchers can create models that replicate the behavior of neurons, neural networks, and brain circuits.
These models help in predicting and explaining experimental observations, leading to new hypotheses and discoveries in the field.
Philosophy of Mind
The philosophy of mind is concerned with fundamental questions about the nature of consciousness, perception, and the mind-brain relationship. Neuroscience and philosophy of mind intersect in exploring these philosophical inquiries through empirical research.
By investigating the neural correlates of subjective experiences, neuroscientists contribute to philosophical debates and shed light on the nature of consciousness. This interdisciplinary dialogue helps bridge the gap between scientific findings and philosophical theories.
Overall, while neuroscience is firmly rooted in biology, it embraces a range of interdisciplinary connections that enhance our understanding of the brain and mind. By integrating psychological science, utilizing chemistry, employing mathematical modeling, and engaging in philosophical discussions, neuroscience continues to expand its horizons and unlock the mysteries of the brain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while neuroscience integrates diverse disciplines, it centers on applying the scientific method to study the biology of the nervous system. Therefore, neuroscience is generally considered a subfield within the biological sciences, even as it pushes the boundaries of interdisciplinary integration.
Its biological foundations and tools predominate.