Is Anthropology A Social Science? Examining The Interdisciplinary Nature Of Anthropology
Anthropology encompasses a broad range of topics related to human beliefs, cultures, and behaviors throughout history. But is anthropology considered a true social science like sociology or psychology?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll examine the interdisciplinary nature of anthropology and look at arguments for and against classifying it as a social science.
If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer: Anthropology is generally considered a social science, though it also draws from the humanities and physical sciences. The study of sociocultural, linguistic, biological, and archaeological aspects of humans makes anthropology a holistic discipline that bridges the social, natural, and applied sciences.
Defining the Field of Anthropology
Anthropology is a fascinating field that encompasses the study of human beings and their societies across time and space. It is often referred to as a social science due to its focus on understanding human behavior, culture, and social structures.
However, it also incorporates elements from other disciplines, making it an interdisciplinary field that draws upon various methodologies and theories.
Four Main Subfields of Anthropology
Anthropology is divided into four main subfields, each with its own unique focus and research methods. These subfields include:
- 1. Cultural Anthropology: This subfield examines the beliefs, customs, and practices of different societies. Cultural anthropologists immerse themselves in the communities they study, often conducting long-term fieldwork to gain a deep understanding of the culture.
- 2. Archaeology: Archaeologists study past human societies by analyzing artifacts, structures, and other physical remains. They use excavation techniques and laboratory analysis to reconstruct and interpret ancient civilizations.
- 3. Linguistic Anthropology: Linguistic anthropologists study the role of language in human societies. They examine how language shapes culture, identity, and social interactions, and explore the diversity of languages across different communities.
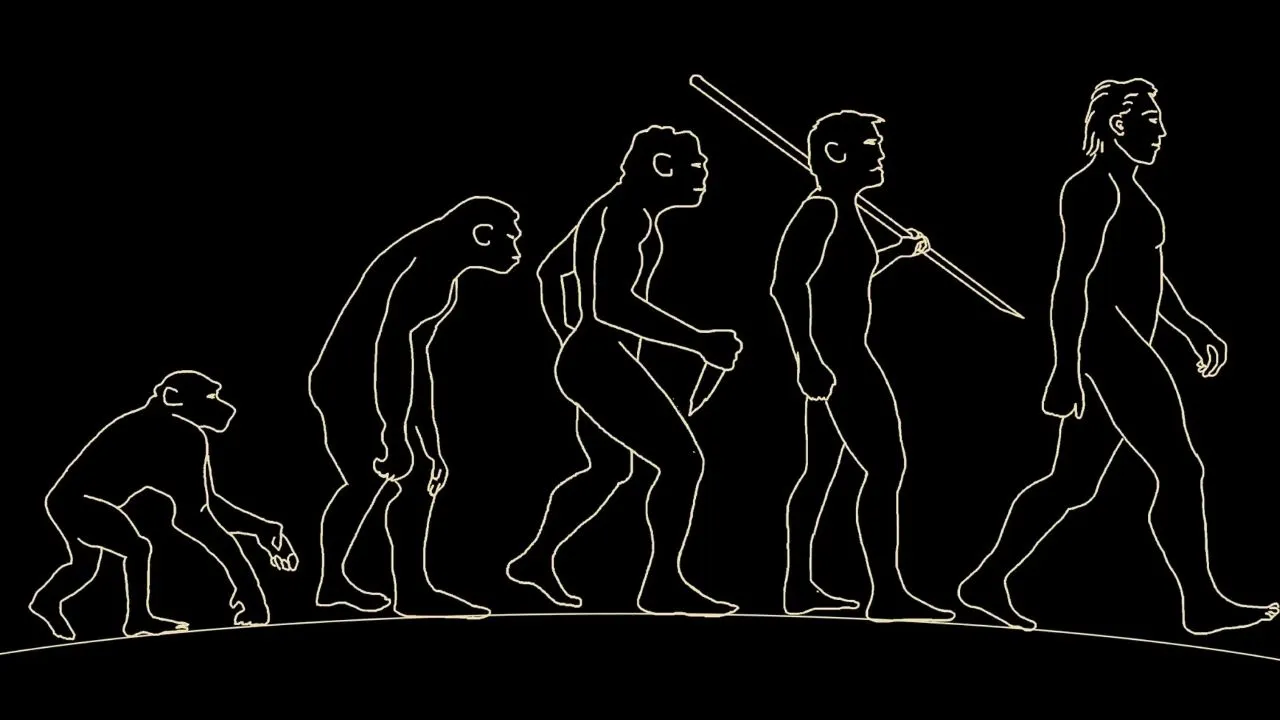
- 4. Biological Anthropology: Also known as physical anthropology, this subfield focuses on the biological aspects of human beings. Biological anthropologists study human evolution, genetics, primatology, and human variation across populations.
Holistic Approach to Studying Humans
What sets anthropology apart from other social sciences is its holistic approach to studying humans. Anthropologists aim to understand the interconnectedness of various aspects of human life, including culture, language, biology, and social structures.
By considering these factors together, they can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the human experience.
For example, an anthropologist studying a particular society would not only examine its cultural practices but also investigate how language shapes social interactions, how biological factors influence behavior, and how social structures impact individual lives.
This holistic perspective allows anthropologists to uncover complex relationships and patterns that may not be apparent when studying each aspect in isolation.
Overlap with Other Social Sciences
While anthropology is often classified as a social science, it also overlaps with other disciplines such as sociology, psychology, and geography. These fields share common interests in studying human behavior, society, and culture, but each approaches the subject from a slightly different angle.
Anthropology’s focus on cultural diversity and its emphasis on understanding the unique perspectives of different societies distinguishes it from sociology, which tends to examine broader social structures and patterns.
Psychology, on the other hand, focuses on individual behavior and mental processes, while anthropology takes a more holistic view that considers both individual and societal factors.
Geography and anthropology also have overlapping interests, particularly in the study of human-environment interactions. Both disciplines explore how humans adapt to and shape their physical surroundings, but geography tends to focus more on spatial analysis and environmental processes, while anthropology examines the cultural and social dimensions of these interactions.
Arguments for Classifying Anthropology as a Social Science
Study of Human Cultures and Societies
One of the main arguments for classifying anthropology as a social science is its focus on the study of human cultures and societies. Anthropologists delve into the intricacies of human behavior, beliefs, and practices, aiming to understand how different societies function and interact.
By examining social and cultural patterns, anthropologists gain valuable insights into the complexities of human society and contribute to our understanding of social dynamics.
Use of Scientific Methodologies
Another compelling reason to classify anthropology as a social science is its reliance on scientific methodologies. Anthropologists employ rigorous research methods, such as participant observation, ethnography, and quantitative analysis, to collect and analyze data.
This data-driven approach allows them to draw conclusions and make evidence-based claims about human behavior and societal structures. By adhering to the scientific method, anthropology ensures the validity and reliability of its findings, further solidifying its place within the realm of social sciences.
Presence Within Social Science Academic Departments
Anthropology’s inclusion within social science academic departments is a strong indicator of its classification as a social science. In many universities and research institutions, anthropology departments are housed alongside other social science disciplines such as sociology, psychology, and political science.
This integration reflects the shared theoretical frameworks, methodologies, and research interests between anthropology and other social sciences. The interdisciplinary nature of anthropology allows for fruitful collaboration and cross-pollination of ideas, enhancing its status as a social science.
According to a study conducted by the American Anthropological Association, 80% of anthropology departments in the United States are situated within social science academic units, further highlighting its classification as a social science.
This close association with other social science disciplines facilitates interdisciplinary research and encourages a holistic understanding of human societies.
For further information on the interdisciplinary nature of anthropology, you can visit the American Anthropological Association’s website: www.americananthro.org.
Reasons Why Anthropology May Not Be Considered a True Social Science
Incorporation of Humanities and Physical Sciences
One reason why some may argue that anthropology is not a true social science is its incorporation of both humanities and physical sciences. While social sciences typically focus on the study of human society and behavior, anthropology goes beyond this and incorporates elements from other disciplines such as archaeology, linguistics, and biology.
This interdisciplinary nature of anthropology can make it difficult for some to categorize it solely as a social science. However, this integration of various fields allows anthropologists to gain a more comprehensive understanding of human culture and evolution.
Broad Scope Beyond Traditional Social Sciences
Another reason why anthropology may not be considered a true social science is its broad scope that extends beyond the traditional boundaries of the social sciences. Anthropology explores not only human society and behavior, but also the physical and biological aspects of human existence.
It delves into topics such as human origins, cultural practices, language development, and even the study of primates. This expansive range of subject matter sets anthropology apart from other social sciences and may contribute to the perception that it is not solely focused on the study of society.
Debate Within the Field Itself
Even within the field of anthropology, there is an ongoing debate about whether it should be considered a social science. Some argue that anthropology’s holistic approach, which combines the study of culture, biology, and language, sets it apart from the traditional social sciences.
Others maintain that anthropology’s focus on human behavior and society aligns it closely with disciplines such as sociology and psychology. This internal debate within the field itself further highlights the complexity of categorizing anthropology as a pure social science.
Conclusion
In summary, anthropology exhibits many qualities of a social science through its examination of human cultures, reliance on scientific procedures, and connections to related disciplines like sociology.
However, its interdisciplinary nature incorporating fields like biology and archaeology makes anthropology distinct. While disciplines can be fluid, anthropology seems to stand at the intersection of science and humanities.
Understanding its multifaceted role can help appreciate this nuanced field that aims to holistically study the human experience.